Using the Push Notifications Service
The Push Notifications service allows you to send native push notifications to different mobile operating systems.
-
Code once and push notifications to iOS and Android.
-
Push notifications to either iOS only or Android only.
-
Push notifications to different variants of a mobile app.
The service supports:
The Push Notifications service offers a unified Notification Service API to the above mentioned Push Network Services. It can be seen as a broker that distributes push messages to different 3rd party Push Networks.
|
Push Notifications Terminology
This section describes terminology that is associated with Push Notifications.
- Push Application
-
A logical construct that represents an Mobile App, for example, Mobile HR.
- Push Notification Message
-
A simple message to be sent to a Push Application.
- Sender Endpoint API
-
A RESTful API that receives Push Notification Message requests for a PushApplication or some of its different Variants. The Server translates this request into the platform specific details and delivers the payload to the 3rd party cloud providers, which eventually might deliver the message to the physical device.
- Variant
-
A variant of the Push Application, representing a specific mobile platform, like iOS or Android, or even more fine-grained differentiation like iPad or iPhone. There can be multiple variants for a single Push Application (for example, Mobile HR Android, Mobile HR iPad, Mobile HR iOS free or _Mobile HR iOS premium). Each supported variant type contains some platform specific properties, such as a Google API key (Android) or passphrase and certificate (Apple).
- APNs
- Installation
-
Represents an actual device, registered with the UnifiedPush Server. User1 running HR Android app, while User2 runs HR iPhone premium on his phone.
- Administrative User Interface
-
(AUI) The Unified Push Admin UI Web UI that allows you manage Push Applications and Variants, view statistics and send Push Notifications to devices.
Setting Up the Push Notifications Mobile Service
Obtaining Firebase Cloud Messaging Credentials
This procedure describes how to obtain Firebase Cloud Messaging Credentials.
Before the Android application is able to receive the notifications, you must set up access to Firebase Cloud Messaging. The following credentials are necessary to set up Firebase Cloud Messaging for your app:
-
Server key
-
Sender ID
-
google-services.jsonfile containing the credentials required to connect your app to Firebase and Google services.
-
From the Project Settings screen, switch to the Cloud Messaging tab, where you can find the Server key and Sender ID (known in GCM as Project Number). There is also a Legacy server key but it should not be used for new projects.
-
Download the
google-services.jsonfile as described in the Google Documentation.
Obtaining Apple Push Notification Service Credentials
This procedure describes how to enable Push Notifications for your iOS application and get the credentials required for push from Apple.
-
Follow the official Apple guide to enable push notifications for your Xcode project.
-
Follow the official Apple guide to generate an APNs client TLS certificate and export the client TLS identity from your Mac.
Make sure to protect the p12 file with a password.
Creating a variant
This procedure describes how to register your app on the UnifiedPush Server
-
Log into the Solution Explorer.
-
Click Open Console beside Push Notification Service.
-
If push applications already exist, they are displayed, click "Create Application" to navigate to the Welcome page. If no push applications exist, the Welcome page is displayed.
-
Click Start Here to dismiss the Welcome Page and go to the Create Application screen
-
Enter a name for your application and click Create App to go to the Variant screen
-
Click Add a Variant
-
Enter a name for your variant and select the platform that you intend to target
-
Enter the Push Network details necessary for your push network and click Create
-
Copy each of the various code snippets into its corresponding file in your application
-
Build and deploy your app
-
Click the Skip the wizard link to finish.
Setting up the Push Notifications Service SDK
This section helps you to set up the Push Notifications service SDK in your App. It describes how to set up and initialize the Push Notifications service SDK.
- Android
- iOS
-
An APNs service.
-
Import the libraries
-
Install
cordova-plugin-aerogear-push:$ cordova plugin add @aerogear/cordova-plugin-aerogear-push -
Install the Unified Push Server package needed for device registration:
$ npm install --save @aerogear/push
Registering device on Push Notifications Service
To receive native push notifications from a Push Network, for example APNs or FCM, the mobile device is identified with a unique device-token assigned by that Push Network. This device-token is passed, by the operating system, to the mobile application. Refer to the operating system and Push Network documentation for further details.
Every time a user launches a mobile app, that app receives the device-token, from a platform-specific method (or callback).
Since the Push Network may assign a new token to a device, AeroGear recommends that the app registers the device-token with the UnifiedPush Server each time.
The required metadata for an Installation:
-
deviceToken: _Identifies the device/user-agent within its Push Network.
-
variantID: The ID of the variant, where the client belongs to
-
variantSecret: Password of the actual variant
The AeroGear UnifiedPush Server is able to store some user-specific metadata as well:
-
deviceType: The device type of the device or the user agent.
-
operatingSystem: The name of the underlying Operating System.
-
osVersion: The version of the used Operating System.
-
alias: Application specific alias to identify users with the system. For instance an
email addressor ausername. -
categories: Used to apply one or more "tags".
The device-token needs to be registered with the UnifiedPush Server, to indicate there is a new Installation for a Variant. This registration is performed by calling an endpoint of the server.
import { PushRegistration } from "@aerogear/push";
new PushRegistration(app.config).register().then(() => {
// Registration with UPS successful, you can now send push notifications from the UPS UI
}).catch(err => {
// Error on device registration
});| Optionally, you can pass the parameters below to the register method |
{
alias: 'some-alias',
categories: ['one', 'or', 'more', 'categories'],
timeout: 5000 // in milliseconds
}Sending a Push Notification using the Unified Push Admin UI
The Unified Push Admin UI allows you to send Push Notifications.
-
Make sure the Push Notifications service is provisioned.
-
Select a route in OpenShift.
-
Login with your OpenShift credentials.
| On first login you need to provide the OpenShift OAuth service permissions to read your user account. |
- Admin UI
-
-
Open the Unified Push Admin UI in a browser.
-
Select the target application from the home page and click Send Notification To This App.
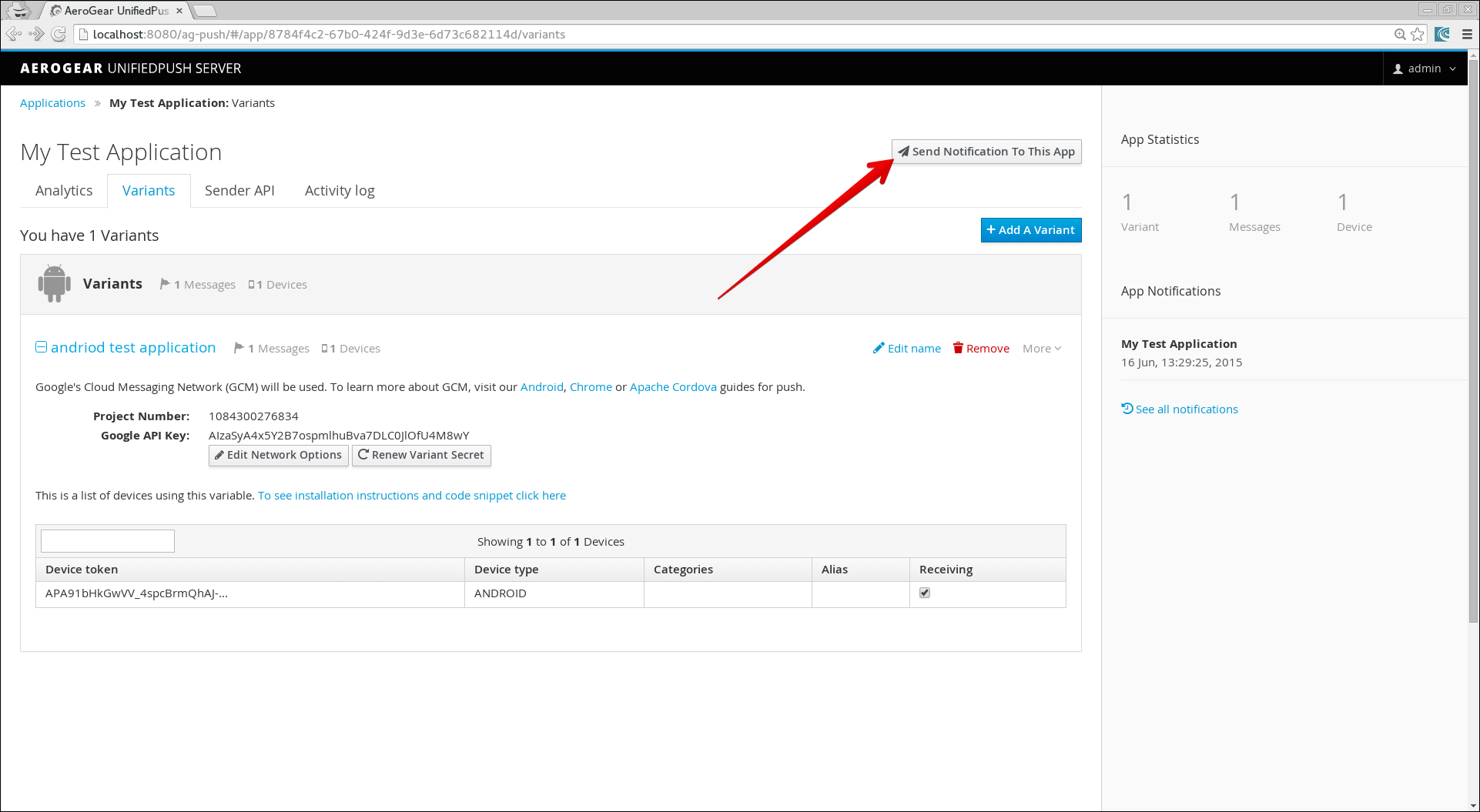
-
When the Send Push dialog displays, enter text in the Message form.
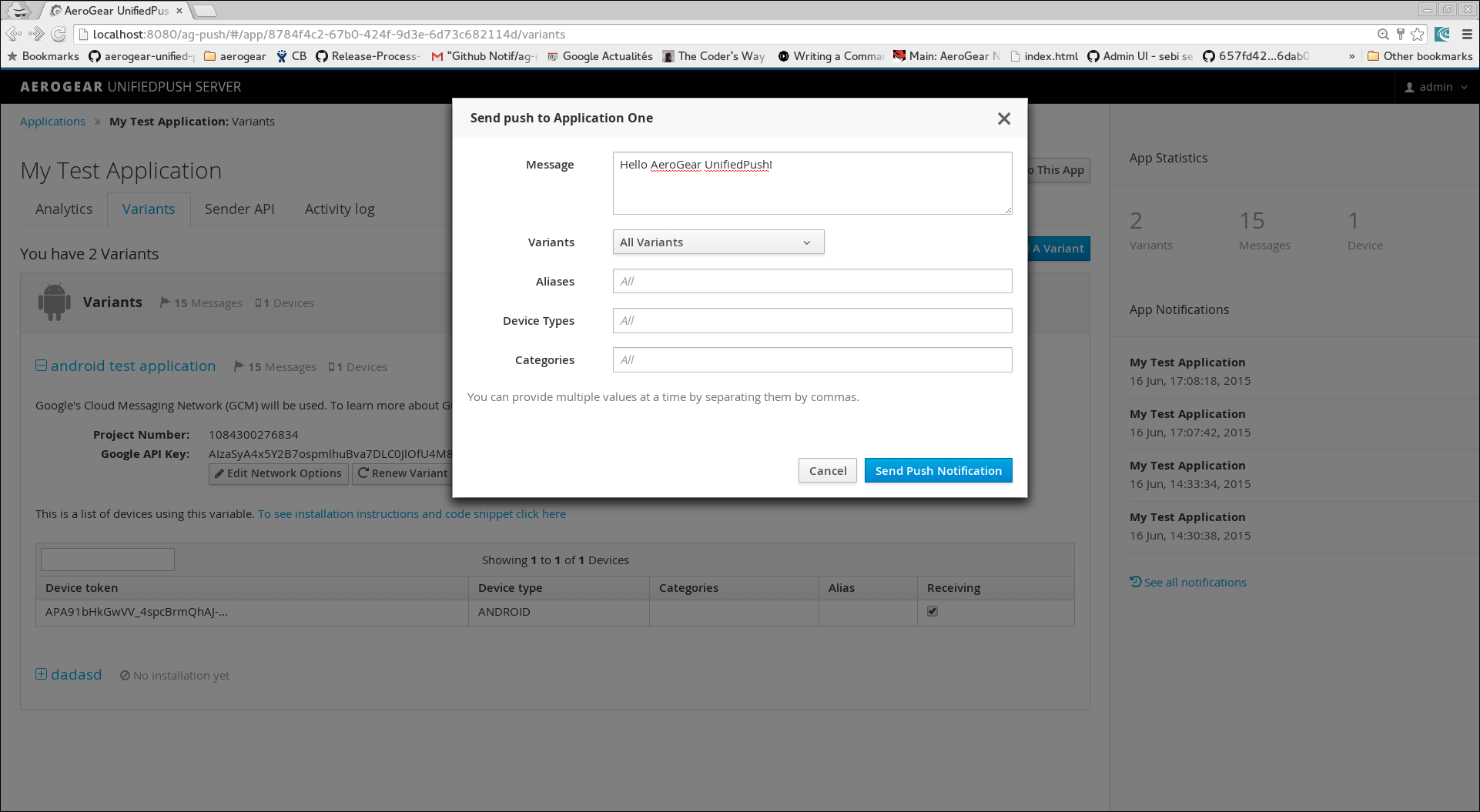
-
Click Send Push Notification to send the message to the target application.
-
- Java API
-
-
Add unifiedpush-java-client as a dependency to your project.
<dependency> <groupId>org.jboss.aerogear</groupId> <artifactId>unifiedpush-java-client</artifactId> <version>[version]</version> </dependency> -
Send the message to the target application.
final PushSender sender = DefaultPushSender .withRootServerURL("<pushServerURL e.g http(s)//host:port/context>") .pushApplicationId("<pushApplicationId e.g. 1234456-234320>") .masterSecret("<masterSecret e.g. 1234456-234320>") .build(); final UnifiedMessage unifiedMessage = UnifiedMessage .withMessage() .alert("Hello from Java Sender API!") .build(); sender.send(unifiedMessage, () -> { //do cool stuff });
-
- Node.js API
-
-
Add unifiedpush-node-sender as a dependency to your project.
npm i unifiedpush-node-sender -
Send the message to the target application.
const agSender = require('unifiedpush-node-sender'); const settings = { url: "<pushServerURL e.g http(s)//host:port/context>", applicationId: "<pushApplicationId e.g. 1234456-234320>", masterSecret: "<masterSecret e.g. 1234456-234320>" }; const message = { alert: "Hello from the Node.js Sender API!" }; const options = { config: { ttl: 3600 } }; agSender(settings).then((client) => { client.sender.send(message, options).then((response) => { console.log('success', response); }).catch((error) => { console.log('error', error); }) });
-
- REST
-
-
Send the message to the target application.
curl -u "<pushApplicationId>:<masterSecret>" \ -v -H "Accept: application/json" -H "Content-type: application/json" \ -X POST -d \ '{ "message": { "alert": "Hello from the curl HTTP Sender!", "sound": "default" } }' \ <pushServerURL>/rest/sender
-
| The 3rd party Push Network is responsible for delivering the Push Notification to the target application. |
Handling Incoming Push Notifications
This section describes how to handle incoming push notifications in your foregrounded application.
| Push notifications that arrive when the application is in the background are always handled by the OS. |
-
Add the following code to your app:
import { PushRegistration } from "@aerogear/push"; PushRegistration.onMessageReceived((notification: any) => { console.log('Received a push notification', notification); }); -
Build and run your app.